The lens is a transparent soft biconvex structure composed of crystallins. The adult lens measures about 9 mm in diameter and is 3.5 mm thick. It is completely enveloped by the thickest basement membrane in the body, the capsule (#1 in photomicrograph ), which is 10-20 µm thick of hyaline material containing type IV collagen. There is a layer of large cuboidal epithelial cells, (the lens epithelium) beneath the anterior capsule (#2 in photomicrograph).

In the center (#3 in photomicrograph) tightly packed cells have lost their nuclei and become packed by special transparent proteins (crystallins) to form so-called lens fibers. New lens cells are added to the margin of the lens throughout life from the lens epithelium, but the cells at the cortex and nucleus (center) of the lens do not undergo turnover or replacement and are therefore the oldest cells in the body of an adult. The lens is avascular and nourished by diffusion from the aqueous and vitreous. The radius of curvature of th
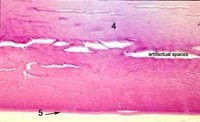
e anterior surface averages 10 mm, but it is subject to marked changes during accommodation. Because the lens nucleus is formed by increasing density of cortical cells, cortex and nucleus are considered together. Both are made up exclusively of cells derived from the lens epithelium. The common designation of “lens fiber” for the cortical cells is a misnomer for the elongated cells of the lens substance. Lens cortical cells are elongated and on cross-section, appear hexagonal in shape. The cortex resembles the cut surface of a honeycomb. In light microscopy, the transition from cortex to nucleus is characterized by less distinct lamellae. The posterior capsule (#5 in the photomicrographs) does not have any epithelium associated with it as the epithelium "migrates" anterior from the lens equator. Below is a photograph at the lens bow. Note the epithelium abruptly stops where the posterior capsule begins. Click to enlarge the photo and then use the back key to return.
 Next topic in Eye Pathology
Next topic in Eye Pathology
